Introduction
What words do you hear the most often when it comes to blockchain? Likely, these are security, decentralization, trust, smart contracts, and cryptocurrencies. They are cornerstones of the business adoption of blockchain, motivating entrepreneurs to unlock new fantastic opportunities for their companies.
However, the devil’s always in the detail, and details of blockchain adoption in business are what I would like to emphasize in this article. They may negate all your efforts and resources intended to bring value to your company when you start incorporating blockchain in a business model.
If you want to utilize blockchain just to say that “My project is secure because it uses Blockchain,” don’t waste your time reading this article. However, if you’re going to use blockchain technology to improve your business and create value for your company and customers, this article may give you all the needed information about it. Here we will consider the four most important points to pay attention in case of blockchain adoption in business, namely:
- Security;
- Decentralization and trust;
- Smart contracts;
- Cryptocurrencies.
Would you like to discover how can blockchain improve business? Let’s take a route across the peculiarities of this technology!
Security

Let’s start with a security question since it is one of the must-have features of mass-market applications. What does security usually mean? This concept includes the following points:
- Hashing sensitive data, such as passwords;
- Data immutability (the ability to edit or delete historical data);
- Data distribution/replication (the ability to replicate the copy of any data to the whole network).
Before you start adopting blockchain for your business, you may ask the following questions:
- Is it possible to implement hashing with any other technology besides blockchain? — Yes!
- Can data immutability be achieved in any other way apart from blockchain? — Of course!
- Can data distribution/replication be implemented using any other technology besides blockchain? — Sure!
These simple questions let us understand that blockchain is not an ultimate tool to solve the above-mentioned issues. First of all, you should know that blockchain can enhance security when all of these points are implemented. Secondly, even if all these problems are tackled, blockchain doesn’t necessarily bring value to your business because it’s also important to consider how it’s implemented. Here is an example of a secure system that brings value to the business (an Ethereum network):
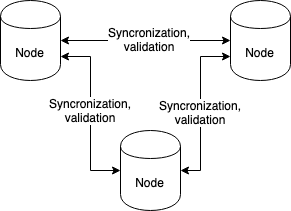
It is secure and valuable because:
- copy of any data is stored on each node;
- all the nodes take part in transaction validation;
- all the nodes are in-sync with each other.
Here is an example of an insecure system:
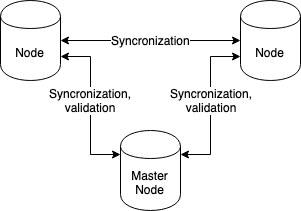
In this system:
-
- the copy of any data is stored on each node;
- one node decides to validate or not validate a transaction;
- all the nodes are in-sync with each other.
Both systems are decentralized because the data is stored on all the nodes in a system. However, the second system has a potential security bottleneck that negates the pros of the decentralization. It means that if you hack the MasterNode, you may gain control over the validation of transactions. So, it depends on the way you define “decentralization” and how deeply you dive into the system you build.
Decentralization and trust

Above, I have provided two examples of systems that differ in terms of security. Now, let’s consider them in the context of decentralization. In order to understand the nature of these systems better, we should answer the following questions:
- Do all the nodes store all the information?
- Do all the nodes participate in the verification process?
- Do all the nodes have the same permissions for the blockchain information?
Here is an example of a private blockchain network:
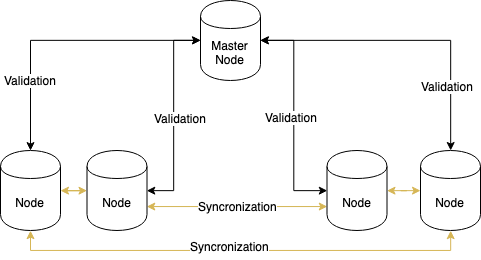
The network can be considered as a decentralized one because the copy of the data is stored on most network machines. At the same time, the network can be considered as a centralized one because there is a single point of authority/trust, which validates the operations conducted between the participants. However, this phenomenon is not a problem, but rather a structure that should be applied in specific cases like any other tool.
Smart contracts
Sometimes customers consider smart contracts as a solution to almost every problem. They think like:
Do you need automation?— Smart contracts may help!
Do you want to build trust? — Smart contracts may help!
Do you want to provide decentralization? — Let’s use smart contracts once again!
However, such a way of thinking may lead to undesired results for your business. To enhance our understanding of the issue, let’s consider the following case:

Each of the blockchain nodes in the system has a copy of the code that looks like “Code XXX” in a picture. One of the nodes has a fragment of a code called “Code YYY.” In this situation, the “Code XXX” may be considered as a smart contract since it is copied to other blockchain participants. The “Code YYY” may not — because it is stored only on one of the nodes and is used only there. Once the code is shared with other nodes and used by them, the “Code YYY” is considered a smart contract.
| Stored and used on one node |
Shared |
Considered as a smart contract? |
| Yes |
Yes |
 |
| Yes |
No |
 |
Of course, the smart contract concept is much wider, but for the article, we can keep it as simple as that.
Cryptocurrencies

It’s unnecessary to always use blockchain to create an application that performs operations with cryptocurrencies. Keep in mind that if your customers need an app that allows selling or buying cryptocurrency, you can implement it without the involvement of blockchain. Several examples provided below will help you better understand how it works.
Example 1: your customer buys cryptocurrency on your website.
The customer specifies his bank card details, cryptocurrency wallet details, and confirms the operation. You receive money to your bank account. Your cryptocurrency partner sends cryptocurrency to the customer’s wallet.
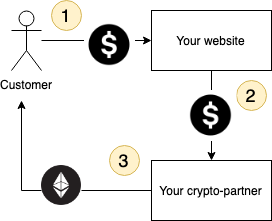
The only essential thing you must be sure about is that you receive and send fiat money safely. It can be implemented via integration with the most popular fiat gateways, like Stripe and others. You are not related to blockchain, it is the responsibility of your cryptocurrency partner. Thus, you do not need any blockchain development.
Example 2: your customer pays for a service with cryptocurrency
Your customer chooses cryptocurrency as a payment method and sends cryptocurrency. Your cryptocurrency partner receives cryptocurrency. Your partner sends fiat to you.
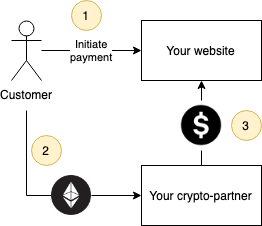
In this example, it is crucial to integrate your cryptocurrency partner with your website correctly. Your customers may be able to pay for goods or services with a particular modal window or your crypto-partner website. Anyway, regardless of a specific method of implementation, your site still isn’t connected to the blockchain.
You may wonder in what cases do you need to use blockchain for cryptocurrency payments? Here are some of them:
- You want to be a part of the blockchain network (utilize a node).
- You don’t want to use any 3rd party services.
- You want to provide your users with a possibility to manage their cryptocurrency balances and operations directly, without any 3rd party/middleman.
- Other cases when you want to perform operations directly in the blockchain and utilize the blockchain’s full capacity.
The Brief Checklist on How Blockchain Can Be Used to Improve Your Business
This article aims to share some of our experiences with you in the most straightforward way so that you could make better-informed decisions and increase the efficiency of blockchain adoption in business. For some of our readers, it is obvious; for others, it looks over-complicated. That’s why I suggest this check-list for your consideration to help you increase the efficiency of your cooperation with the blockchain software development team:
- Specify business requirements, not technical specifications.
- Delegate the technical decisions to the developers, do not interfere, and validate the arguments that drive their decisions.
- Find a person with an extensive technical expertise to review the developers’ choices.
Here are some examples:
| # |
Do  |
Don't do  |
| 1 |
Specify the task like here: “I want to provide my customers with the possibility to pay for goods with the most famous cryptocurrencies on my website” |
Don’t specify the task like in the example: “Integrate ERC-20 standard into my website payments” |
| 2 |
Ask the following questions: “Why do we have Master Nodes? I haven’t seen them in the Ethereum architecture, and I thought that we planned to do something like that. Can we delete them from the architecture? What will it lead to? |
Don’t ask to do the next: “I’ve seen an Ethereum architecture, there are no Master Nodes. Delete the master nodes from the architecture, but keep the same functionality.” |
| 3 |
Delegate the review of technical decisions to a special person loyal to you |
Don’t review all the technical decisions and approve/decline them on your own, even if you don’t have any expertise. |
Conclusion
The blockchain has disrupted many industries and made businesses rethink their operations. However, to implement it for your companies successfully, you must be aware of the pros and cons of this technology as well as to be well-informed about all the pitfalls of the blockchain development process. Hopefully, this article has shed light on the issue and will help you understand how blockchain technology can improve the way companies do business.
Would you like to innovate your business by incorporating blockchain technology? Then, you need to find great blockchain developers who can help implement it at the highest level. Since 2014, S-PRO has worked as a strategic technology partner with many startups, SMBs, and enterprises all over the globe and can help you meet your business goals using blockchain. This year, our expertise in blockchain development has been recognized on a global scale by GoodFirms. Don’t hesitate to reach our experts to discuss your project.
How enterprises use artificial intelligence













