The term Big Data has been widely heard for many years. But not everyone has an exact idea of what this concept represents. The easiest way to explain it to an uninformed person is to explain with a practical example.
For instance, the analysis of big data allows you to display ads only to those consumers who are interested in a product or service. Take a look at the way it works in our article about DMP.
Another curious case has happened several years ago. The Target retail chain began to use big data and machine learning while interacting with customers. The algorithms analyzed how and under what conditions customer preferences have changed and made predictions. Based on these forecasts, customers received all kinds of special offers.
Once a schoolgirl’s father complained that his daughter got booklets with suggestions for pregnant women. Later it turned out that the girl was indeed pregnant, although neither she nor her father at the time of the complaint knew about it. The algorithm has caught changes in customer’s behavior that are specific for pregnant women.
Big Data Essentials: The 5 V’s You Need to Know
Most often, the main definition of big data is the well-known “3V” (Volume, Velocity, and Variety), which was introduced by analyst Gartner Doug Laney in 2001.
The Signs of Big Data
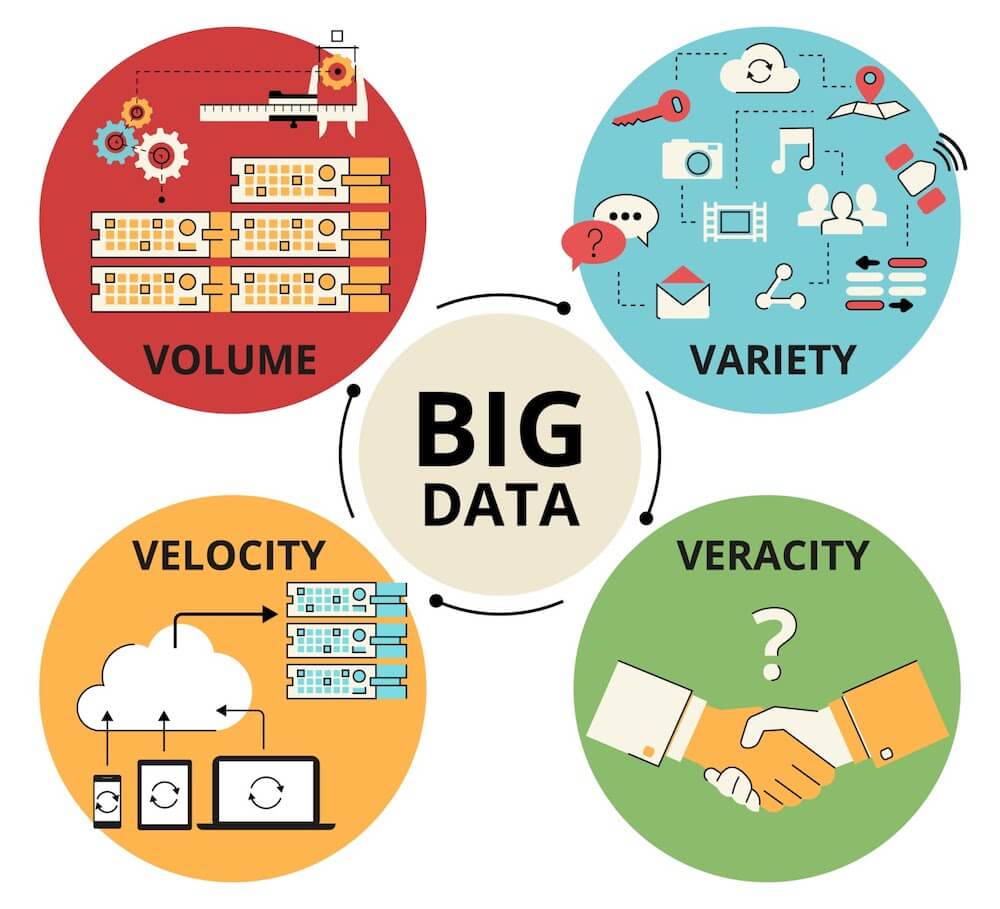
The first 3 V’s of big data (Volume, Velocity, and Variety) were initially suggested by Gartner in 2001 to describe the key characteristics of the concept as well as the possible challenges the large datasets pose. Over time, as the field matured, and more and more knowledge was accumulated, 2 additional V’s were added — Value and Veracity.
Volume in big data stands for the amount of general data that exists and can be gathered and analyzed. There’s really no one set amount of datasets needed to define the data as big. Especially now that we also have the concepts of wide and small data. But generally, the volume of the information or data sets should be too large to be able to work with them using a computer or a desktop processor. This comes both as an opportunity and a challenge for organizations working with big data. On one hand, it gives immense knowledge and insights into the market and consumers that the companies can use for their benefit. On the other hand, handling such amounts requires investing in robust solutions that can be scaled on short notice.
Velocity in big data is another key characteristic that tells us more about the features of large datasets. It refers to the speed of the data flow needed to generate and move through the stages. The sources of such information can be social media, smartphone actions, and transactions — all the things that appear momentarily. In all these cases, it’s important to quickly collect and analyze the datasets. For some fields, this is more important than for others — for example, the healthcare sphere. Within this area, organizations often collect their information from wearable devices and medical equipment. This data needs to be quickly scanned and analyzed. However, Velocity adds to the challenge — some argue that it’s better to have less data with fast velocity than more data with slower velocity.
The next pillar of the initial 3 V’s is Variety. As the name suggests, it refers to the diverse types and formats of sets that comprise big data. As the organization can get the information from various sources, their types can differ as well. The main ones include:
- structured data (databases and spreadsheets),
- unstructured data (text, images, and videos),
- semi-structured data (XML, JSON data formats).
Sometimes the raw data is added to the category tree — it includes all the data that hasn’t been processed at all, although it can also fall into any of the first three categories depending on the received format. The main challenge of this characteristic is standardization and further distribution of the collected data.
Veracity is about the quality, accuracy, and credibility of the collected data. It became a concern when organizations started to gather vast amounts of unstructured data from various sources, as it often comes messy, confusing, and sometimes lacking pieces. This is a problem since such data can lead to incorrect insights. It is especially important for healthcare because people’s lives depend on such data, and gathering incomplete info about the medications taken or allergies can lead to health issues and deaths.
Value covers the benefits organizations can get by using big data. It mostly focuses on the outcomes — the results from data processing, which can give insights and support decision-making. Furthermore, it is often a challenge since the results from big data are also big, and it can be difficult to prioritize them. Each organization operating on such scale should have its own unique way of deriving insights from vast amounts of information.
Lately, there’s been talks about the 6th V — Variability. This characteristic refers to the inconsistencies within the data and the need to manage the data flow correctly to decrease any variability.
What are the benefits of Big Data for business?
In the fundamental document “Big Data: The Next Frontier for Innovation, Competition, and Productivity”, which in its time sharply raised global interest to Big Data, McKinsey identified 5 ways where big data creates value:
– Transparency – quick access to the necessary information can significantly reduce the time of operating activities and improve quality.
– Ability to experiment to identify needs, determine variability and increase productivity.
– Population segmentation to customize actions for a specific audience. Thanks to the wide capabilities analysis of Big Data, customer interaction will be even more personalized and targeted.
– Replacing or supporting a person’s decision making by algorithms.
– Creation of new business models, products and services.
Big Data and Machine Learning
What is the easiest way to understand how business learning models are applied to business? How are Big Data and Data Science connected?
Imagine a robot, which claims it can solve the most difficult tasks.
Solving such tasks immediately is unreal. The machine needs to write millions of rules and exceptions – so it does not work like that.
They do it otherwise – robots are trained on data, for example about your clients. They are learned to analyze, extract useful patterns and somehow use them. Here such disciplines as statistics, machine learning, and optimization will help us. And if you have already had Big Data, then the robot can potentially become even smarter – ahead of the competitors’ decisions not only in speed but also in the quality of solutions. Put simply, the more data we have, the more intelligent your robot can become.
Is there hype around Big Data?
The analytical company Gartner that studies trends and annually releases the Gartner Hype Cycle chart, which assesses the development and popularity of technologies, already in 2014 excluded “big data” from the “hype” list, explaining that these technologies had already become a standard for corporate IT.
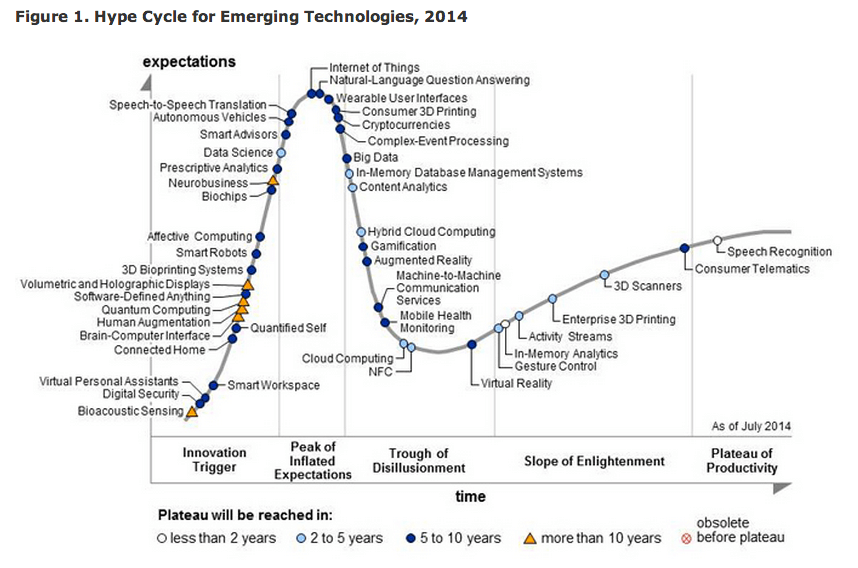
According to experts, businesses looking ahead will be required to use Big Data, otherwise, they will be absorbed by more efficient market players. Increasing the competition level causes the need to improve efficiency.
Big Data – is it expensive?
The fact that Big Data is already a “yesterday hype” has many positive points. Currently, Big Data is considered not as something self-sufficient, but as only one of the tools for solving specific applied problems. Technologies of working with big data from rare and expensive became quite affordable. Open source code may solve the majority of tasks. In order to deal with big data, you should also pay attention to cloud providers, such as AWS, IBM, Azure, etc. with their platforms and services. Under this approach, POC or MVP engineering will take a few days and will require a relatively small budget.
Big Data Market Size in 2024
Although Big Data is no longer a hype word, its market continues to grow. More and more businesses recognize the value of collecting and analyzing vast volumes of data to receive insights into clients’ behavior and trends, optimize internal processes, and stand out among the competition.
Statista’s forecast says that the global big data market size is expected to grow to over 100 billion U.S. dollars by 2027. In 2024, this number is projected to be around 84 billion dollars. Other associated technologies will contribute to the development and growth of this market. They include mobile data and cloud computing traffic, subsequent development of Artificial Technology, Machine Learning, and the Internet of Things. We already use them but with big data volumes, we are just starting to understand their true potential.
Another point of view was released by Gartner not that long ago. They say that by 2025, around 70% of businesses and organizations will “ditch” big data and move to small and wide data. The former refers to the use of smaller data sets and fewer volumes for data analytics. This approach includes datasets that contain a limited number of observations and records. It often consists of information collected from transactions, surveys, records, and customer feedback. Basically, small data is used to support a smaller scale of decision-making, which can later be utilized to analyze local trends and clients’ preferences and offer a more personalized approach.
Wide data is used for the analysis of various unstructured and structured data sources of different sizes. Such datasets contain numerous variables and attributes to each observation. Although wide data may not have as many observations as small data, it can have numerous features for each observation. Wide data is common for fields such as genomics, sensor data, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications, where multiple measurements or attributes are collected for each entity or event. Wide data formats can include text, image, audio, voice, video, temperature, or even smell and vibration.
Gartner believes that these technologies can be used for demand forecasting in retail, and real-time behavioral and emotional patterns can come in handy in customer service, which can later be applied to hyper-personalization and customer experience improvement. Other areas of use can include security or fraud detection, and different mechanisms and adaptive autonomous systems (like robots) that can learn by themselves.
TOP 5 Big Data Technologies and Tools in 2024
The big data field is incredibly fast-growing and still continues to evolve at a crazy pace. New technologies and tools appear on the market every day, and it takes dedication to be able to keep up with them. The largest number of popular new tools were open-source frameworks, a lot of them released by Apache Software Foundation, which oversees the development of open-source projects. Others include NoSQL Databases, which can store and manage vast amounts of data. Let’s take a look at a few tools that will be associated with big data in 2024.
- Hadoop is an open-source framework for storing and processing data. Its MapReduce programming model and Distributed File System (HDFS) allow organizations to store and analyze massive datasets in a cost-effective and scalable manner. It also supports a lot of data processing tools that can be integrated into it.
- Spark is also an open-source tool — basically a processing engine for big data analytics. It offers in-memory computation and support for different programming languages and tasks, like batch and stream processing, machine learning, and graph analytics. It is 100 times faster than MapReduce made by Hadoop.
- Apache Flink provides powerful capabilities for real-time data analytics and applications. It offers a data flow engine that can process continuous data streams in real time. Flink processes streams as a continuous flow of events instead of handling data in batches like other tools do.
- MongoDB is an example of a NoSQL Database widely used due to its scalability, flexibility, and ability to store different types of data — unstructured and structured. Its main difference from traditional databases is that it stores information in JSON format with dynamic schemas. This allows it to easily handle complex and diverse datasets.
- Cassandra is another NoSQL database management system developed by Apache. It is known for high scalability and decentralized architecture, which makes it a perfect choice when it comes to datasets requiring large throughput and low latency. It is widely used in different industries and applications including analytics, IoT, messaging, and transactional systems.
These and many other big data technologies already assist organizations with data collecting and processing and help to cope with challenges associated with the 5 V’s of big data. These tools are just a small part of the big industry that grows and develops with every passing day.
Conclusion
As already mentioned, Big Data is a combination of technologies that are designed to perform three main operations:
- process large amounts of data compared to “standard” scenarios.
- be capable of processing the rapidly incoming data in very large volumes.
- should be able to work with well- and poorly structured data in on various aspects simultaneously.
The main reason why everyone wants to work with these technologies is the growing amount of information generated by mankind exponentially. As well as the fact that on such large samples the laws of averages begin to act that it is possible to reveal many previously hidden patterns. In its turn, this fact opens up a wide scope for their diverse analysis.



