Task-oriented dialogue systems may solve various problems. These systems can be used to book a ticket, order food or schedule a call and are designed to help users with their requests.
Put it simply, dialogue systems are computer systems able to communicate with a human via text, speech, gestures, graphics, and other means. They are also known as Conversational Agents.
How do dialogue systems work?
When we receive an input from the user the first thing we need to do is to recognize what does the user want, which is called an intent classification task.
For example, a user asks “I want to book a ticket from New York to San Francisco for tomorrow”. We should recognize it as a “flight ticket booking” intent.
The next step is to extract relevant information (slots) required for actually booking the ticket, e.g. using third-party API. This data might include flight origin, flight destination, and date of departure.
This task is known as slot tagging and it can be solved with different techniques, one of which is to use Deep Learning to train slot tagging jointly with intent classification task using Convolutional (CNN) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN). Thanks to Memory Networks, RNN additionally can capture context and take into account what the user asked previously in a dialog. Intent classification and slot tagging are often referred to as Natural Language Understanding (NLU).
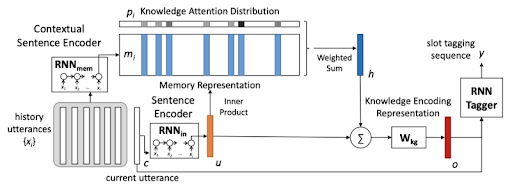
Memory Network for capturing dialog context (source: Microsoft)
Information obtained with the NLU module is then used by the Dialog Manager (DM) to provide a response to the user. Dialog Manager is responsible for dialog state tracking and dialog policy.
State tracking is a process of managing information about what the user currently wants and what is required to help him with his needs.
For example, if a user asks “Book me a ticket from New York for tomorrow” dialog manager tracks intent of “flight ticket booking” and 2 filled slots: origin = New York, date = tomorrow (both intent and slots obtained by NLU), this information becomes dialog state.
Dialog Policy is responsible for taking an action based on the current state of the dialog. At this point Dialog Policy knows that to book a flight we need to also know destination, which is required slot, so it asks user “Where do you want to go?” and user responds with “San Francisco” which is recognized by the slot tagger as destination = San Francisco, and Dialog Manager adds it to the current dialog state. Now Dialog Policy is happy with all slots required to fulfill this intent being filled and it decides to query third-party API for available tickets and shows them to the user. In general, Dialog Policy can ask the user for additional information, request some external resources or just give him an answer.
Dialog Manager can be built using hand-crafted rules or Deep Learning-based approaches, e.g. trained jointly with other tasks, such as NLU. Also, we can build Dialog Manager using a combination of methods, for example, handcrafter rules for Dialog Policy and Deep Learning for State Tracking.
How does business use dialogue systems?
Dialogue systems have great potential to automate a wide range of processes in business. Let’s check the most common use cases!
- Interactive self-service for customers
Potential clients may find the answers to the most common questions about a company’s services or products through a special form on the website or in a mobile app.
- A knowledge base for staff
Allows agents to retrieve and use efficiently the troubleshooting information, faqs, user manuals, etc. thus enhancing the operations.
- Guided selling
Dialogue systems can help potential buyers to choose the best product or service according to their needs and guide to the actual purchase. Business, in its turn, receives a simpler process of guiding potential customers to a buying decision and thus an increased conversion rates.
- Internal help desk
Company’s employees receive the answers related to the internal issues instantly: HR questions, equipment inquiries, schedule, etc.
- Website navigation
Users get clear guidance towards the necessary website page or info block.
- Technical support
Customers may solve technical problems with a useful tool that can promptly diagnose each issue related to a product or device.
- Personalized service
Dialogue systems can consolidate multiple databases to provide personalized help for every single customer.
- Educational help
Customer may receive training or bits of advice concerning more efficient use of product or services.
- Interactive voice response
Besides texting support, a customer can get a voice help using speech synthesis regarding the most common questions. Sometimes conversational agents may appear as artificial characters while having an interaction with a customer.
So how may business benefit from dialogue systems?
Taking into account all the applications of dialogue systems, the benefits for business commend themselves:
- Reducing the human factor;
- Saving on human labor;
- Enhancing the speed of operations;
- 24/7 availability for customers;
- Processing more clients’ inquiries;
- A personalized approach to the customer that enhances the client’s trust and increases the conversion rate.
These are the most common advantages of dialogue systems for businesses. There are many more. You’ll identify them straight away after getting to implement them in your business routine. Surely the most prominent role conversational agents play for business is improving customer satisfaction, experience and retention meanwhile reducing costs.
Conclusions
There are many potential applications of task-oriented dialogue systems in various business niches aiming to assist its customers via natural language conversation.
Surely this area carries a bunch of challenges ahead. Although the faster businesses start adopting AI technologies in their everyday routine the more benefits they will gain over time. We’ll continue introducing AI and ML to you in future articles. Stay tuned!




