It seems that nowadays everyone is talking about blockchain, bitcoin, and ICO, but the reality is different – most people are far from understanding it. So it’s natural to ask about what it really is.
The blockchain definition may seem too complex. Most materials about this technology are hard to understand for a random person. They dive deep into technical aspects. Well, the truth is understanding what blockchain does is much more important than how it does those things. So now is the moment for us to explain in plain English, what blockchain technology is all about.
Blockchain – what is it?
Blockchain is like a shared and open diary containing all the records that can’t be modified. Each time someone buys or sells coins or goods, all the details like its sender, recipient and date/time – are added to what is referred to as a block, often in an encrypted fashion, to protect it from cybercriminals. These transactions are also recorded and processed without a third-party provider, which is usually a bank.
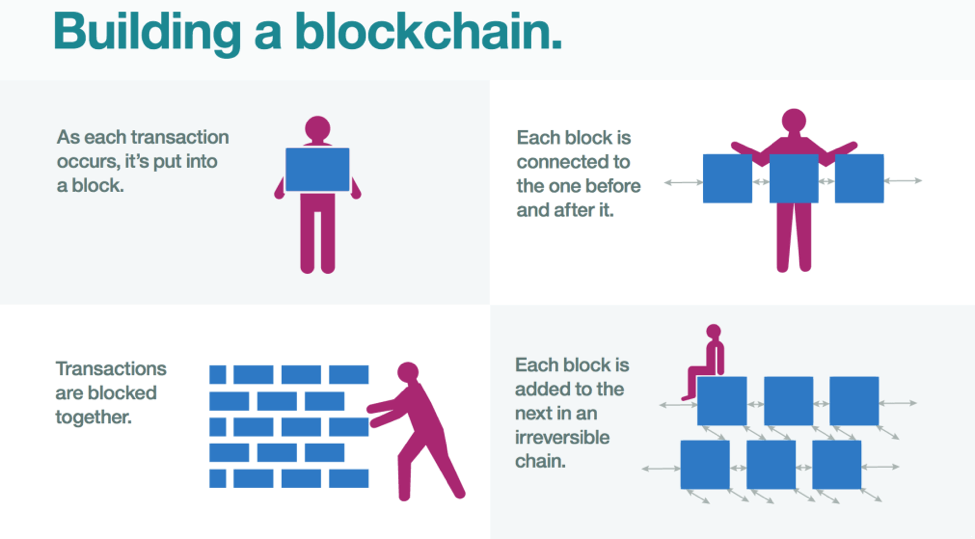
Blockchains flow (IBM)
Blockchain makes transactions safe and reliable. It doesn’t even matter whether people trust each other. It cares about security a lot.
Nowadays there are many debates over the way blockchain can completely change the way digital transactions are conducted. In perspective, it has the power to change the way many industries conduct their daily routine.
How does it work?
Each transaction is digitally signed which ensures its authenticity and security. What’s really fascinating is the way transactions are being distributed among all the parties in the network.
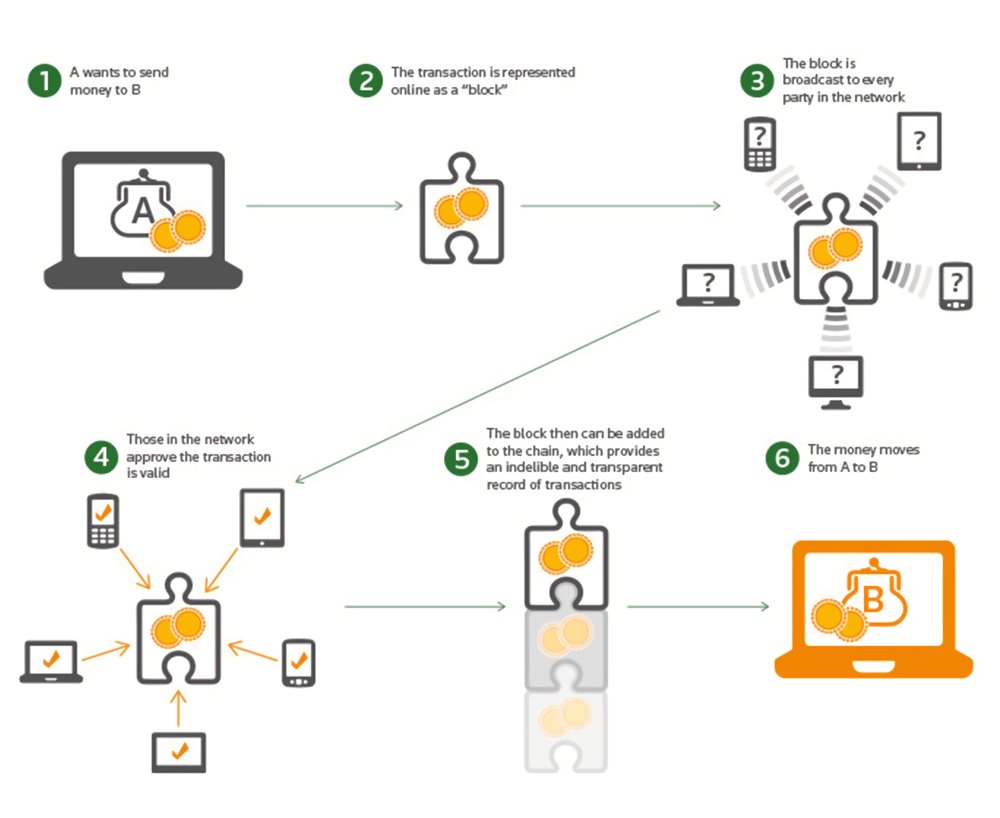
All transactions performed in blockchain are spread among a large number of computers all over the world. These computers are called nodes. Those nodes have the power to provide a consensus about the validity of each transaction at any moment.
When a new transaction goes into a blockchain a majority of the nodes should evaluate and validate the history of the individual blockchain block that is offered. Each party has its copy. If there is a consensus among parties that the history and signature are valid, the transaction is accepted, added to a new block which in its turn is added to the chain of transactions.
In case a majority does not agree with that transaction, it is denied and can’t be added to the chain. This distributed consensus model is the essence of blockchain. It helps to run a distributed ledger without the need for some central authority defining what transactions are valid and which ones are not.
By the way, if a party tries to change a piece of data, all the other computers have the original hash so they won’t allow to change it.
Below is the algorithm of how blockchain works in the most widespread situation when someone wants to pay for some value.
Blockchain transaction – what is it?
To carry out a transaction a party needs 2 things: a wallet (public key) and a private key. A wallet is a string of digits and letters, also called a public key. It is an address that appears each time a transaction is done. The private key is a string of random digits that should be kept in secret.
When someone enables a transaction it should be signed with a private key, which is only visible to a sender. Then a network of nodes carries that transaction making sure that it is valid. Once it confirms its validity the transaction is put into a block where it can’t be changed anymore. Here is the structure of a random transaction with keys.
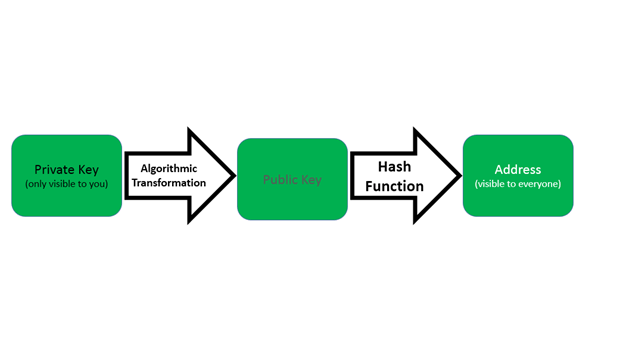
Special protocols make sure that the blockchain network works the way it was meant to be—as a distributed, peer-to-peer and secured information database. A protocol is an individual behavior specification with a large set of rules which is programmed into it.
Blockchain security
Among the most important problems of today’s digital economy, online security seems to take the first place. That’s where blockchain stands out. It’s not like with banks. The blockchain eliminates the risks that centralized institutions have by storing data across the network nodes.
To transfer any value the network of computers should first agree on the transaction validity. So to hack this system you would have to hack each and every node on that network, which size is enormously huge.
Of course, being an emerging technology, blockchain has some challenges ahead. As an analysis of a blockchain can often be traced back to an individual sender or receiving funds. That’s just one of the aspects. In general, blockchain technology is significantly better than anything created before.
Where it is used now?
IoT. Transport. Government. Health. Finance. Insurance. Media. Blockchains are being put to a wide range of uses in lots of spheres.
In the transportation sphere, for example, it will allow car owners to pay on-the-go for all the known fees for parking lots, car-sharing, charging, etc. Also, it will give the ability to integrate with smart systems which make it possible to control the car’s charging process anywhere at any given moment.
There are various applications of blockchain that can help in the government sphere and in this way take the existing model of e-government to the next level. This includes e-voting, home security, and electronic citizen ID cards.

For example, Estonia citizens and e-residents have access to most public services with a secure ID card that functions with blockchain. Citizens can check their records in government databases and see who has access to them.
What are the main problems of blockchain?
Every emerging technology has barriers to overcome.
Some say blockchain is overhyped and in reality has limitations in use and drawbacks in security. But it has gone through a lot already: lots of trials, researches, extreme development. So now we have a picture of blockchains limitations.
-
Complexity
Blockchain technology requires an absolutely new approach.
Cryptography is full of new jargon. Although there is a growing number of glossaries and indexes that make it easy to understand.
-
Network size
To prevent hacker attacks and become stronger blockchain requires a large network of users.
The more it is distributed among the bigger number of nodes the better. For blockchain, but what about the real projects? Will they handle the quantity? There are debates being held from time to time about whether this is a fatal issue for some blockchain projects or not.
-
Human error
Being used as a database, blockchain requires high-quality pieces of information put into this database.
No mistakes should be taken. As these ones would be extremely hard to change.
-
Unavoidable security flaw
If more than half of the computers working as nodes in the network tell a lie, this lie will become the truth—the most important security flaw in blockchains.
For this reason, blockchain transactions should be monitored by the whole community, ensuring no such thing happen and that no one can gain this big influence.
-
Politics
Blockchain has all the power to digitize government sphere forming another type of governance model via miners. Thus it may cause public disagreements between different community sectors.
These debates are clearly noticeable around the question or event of ‘forking’ a blockchain, a process of the blockchain protocol update when a majority of a blockchain’s users have agreed to it. Although this offers new opportunities for governance experimentation that might take this sphere to the next step.
As you see, blockchain limitations are relative and can be overcome eventually. What’s more important is the benefits it holds for not just business, but also for each person living on planet Earth.
Conclusions
This is just the beginning. Potential blockchain uses are limitless and the new ones are being discovered on a regular basis.
The technology can serve almost any type of transaction which involves value, money, goods, and property.
The main power lies in its abilities of not requiring trust and being decentralized. This will reduce fraud greatly and will have a hugely magnificent impact on the whole society and the global economy.
The most exciting applications haven’t even been invented yet!





